The scoops deal with published (classical or OPEN) and grey literature (blogs, websites, social networks, press releases) allowing rapid access to recently published relevant information
May 29, 2015 you were 26796 visitors, viewing this topic 34.5K times., 4900 scoops
June 2020 : >7.3K scoops, >94.5K visitors, #121K views
August 2022: >7.8K scoops, >96,2K visitors, >133,7K views
December 2023: >8K scoops, >97,7K vis, >171,3K views



 Your new post is loading...
Your new post is loading...





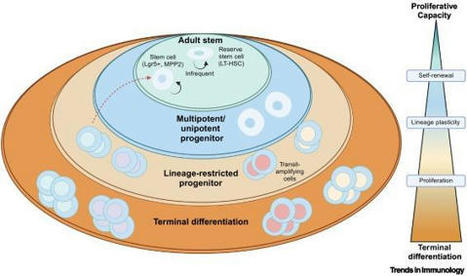

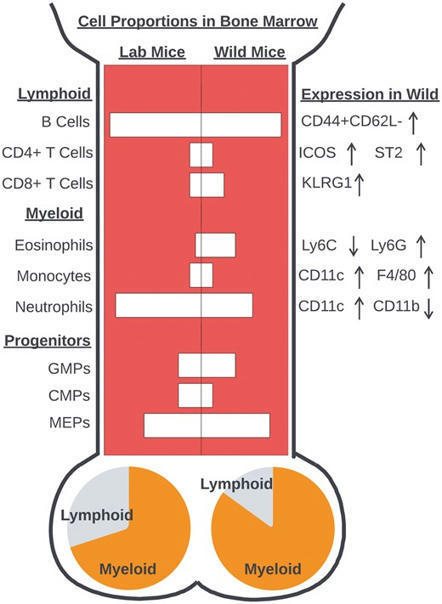

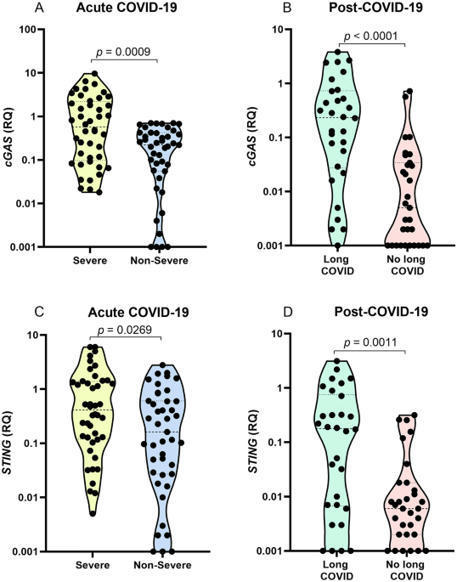
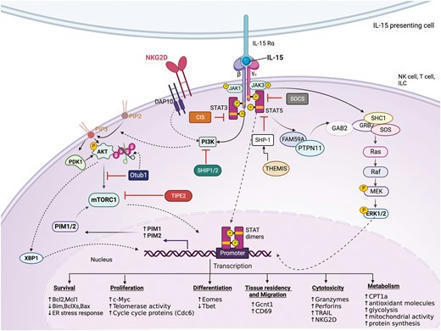
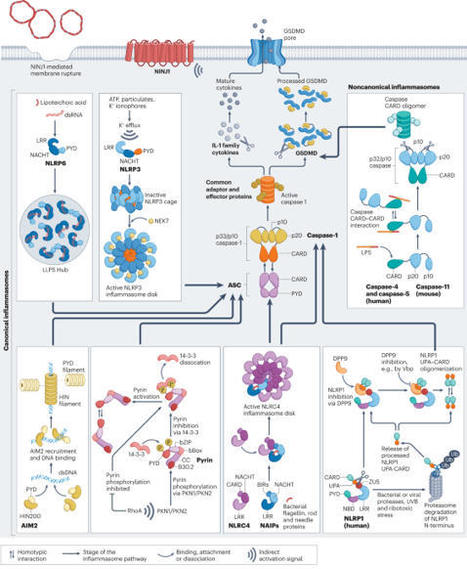
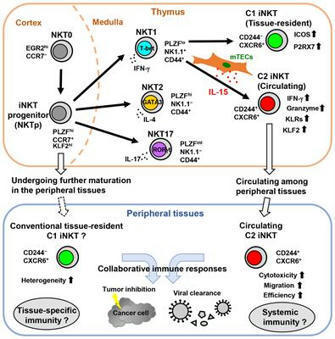


This topic is focusing mainly on fundamental systemic immunology.
Some subjects are particularly adressed, according to my personal interests in research or teaching, for instance
Lymph node
https://www.scoop.it/topic/immunology?q=lymph+node
Feel free to browse other related topics!
Mucosal Immunity:
http://www.scoop.it/t/mucosal-immunity
Immunology and Biotherapies
http://www.scoop.it/t/immunology-and-biotherapies
Autoimmunity
http://www.scoop.it/t/autoimmunity
Allergy and clinical immunology:
http://www.scoop.it/t/allergy-and-clinical-immunology
History of Immunology
http://www.scoop.it/t/history-of-immunology
and more recently
Fake News and Vaccinations
https://www.scoop.it/topic/assim-actualites