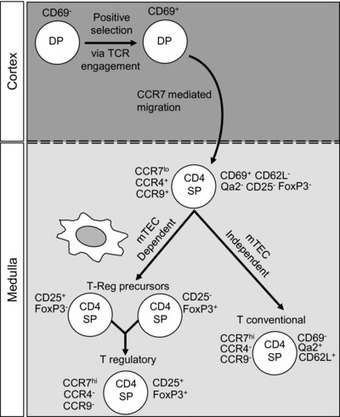
The organization of the thymus into distinct cortical and medullary regions enables it to control the step-wise migration and development of immature T-cell precursors. Such a process provides access to specialized cortical and medullary thymic epithelial cells at defined stages of maturation, ensuring the generation of self-tolerant and MHC-restricted conventional CD4+ and CD8+ αβ T cells. The migratory cues and stromal cell requirements that regulate the development of conventional αβ T cells have been well studied. However, the thymus also fosters the generation of several immunoregulatory T-cell populations that form key components of both innate and adaptive immune responses. These include Foxp3+ natural regulatory T cells, invariant γδ T cells, and CD1d-restricted invariant natural killer T cells (iNKT cells). While less is known about the intrathymic requirements of these nonconventional T cells, recent studies have highlighted the importance of the thymus medulla in their development. Here, we review recent findings on the mechanisms controlling the intrathymic migration of distinct T-cell subsets, and relate this to knowledge of the microenvironmental requirements of these cells.
Via Krishan Maggon


 Your new post is loading...
Your new post is loading...








Mini-Review
Thymus medulla fosters generation of natural Treg cells, invariant γδ T cells, and invariant NKT cells: What we learn from intrathymic migrationAuthorsJennifer E. Cowan, William E. Jenkinson, Graham Anderson First published: 13 February 2015Full publication historyDOI: 10.1002/eji.201445108