Abstract
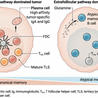
Interleukin 10 is a cytokine with the ability to reduce or terminate inflammation. Chronic viral infection, such as infection of chronic hepatitis B, hepatitis C and HIV, has increased levels of interleukin 10 in peripheral blood. Serum IL-10 levels are also high in certain cancers. Blocking IL-10 signalling at the time of immunisation clears chronic viral infection and prevents tumour growth in animal models. We review recent advances in this area, with the emphasis on potential use of this novel strategy to treat chronic viral infection and cancer in human.
Via Krishan Maggon


 Your new post is loading...
Your new post is loading...







•IL-10 signalling blockade at the time of immunisation clear chronic viral infection.
•IL-10 signalling can inhibit or promote tumour growth.
•IL-10 signalling inhibitors are under development.
•Potential side effects of IL-10 signalling blockade.