 Your new post is loading...
 Your new post is loading...
The authors show that early Th2 cell differentiation is driven via prolonged T–DC macro-clustering in lymph nodes and occurs in a skin site-specific manner
Dendritic cell (DC) subsets with biased capacity for CD4+ and CD8+ T cell activation are asymmetrically distributed in lymph nodes (LNs), but how this affects adaptive responses has not been extensively studied. Here we used quantitative imaging to examine the relationships among antigen dispersal, DC positioning, and T cell activation after protein immunization. Antigens rapidly drained into LNs and formed gradients extending from the lymphatic sinuses, with reduced abundance in the deep LN paracortex. Differential localization of DCs specialized for major histocompatibility complex I (MHC I) and MHC II presentation resulted in preferential activation of CD8+ and CD4+ T cells within distinct LN regions. Because MHC I–specialized DCs are positioned in regions with limited antigen delivery, modest reductions in antigen dose led to a substantially greater decline in CD8+ compared with CD4+ T cell activation, expansion, and clonal diversity. Thus, the collective action of antigen dispersal and DC positioning regulates the extent and quality of T cell immunity, with important implications for vaccine design.
If you thought finding a needle in a haystack was hard, try maneuvering a T lymphocyte through the “three-dimensional meshwork” that makes up t
T cells exhibit high-speed migration within the paracortical T zone of lymph nodes (LNs) as they scan cognate Ags displayed by dendritic cells in the tissue microenvironment supported by the network of stromal cells.
|
bioRxiv - the preprint server for biology, operated by Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, a research and educational institution
The influx and efflux of cells and antigens to and from the draining lymph nodes largely take place through the subcapsular, cortical and medullary sinus systems. Recent analyses in mice and humans have revealed unexpected diversity in the lymphatic endothelial cells, which form the distinct regions of the sinuses. As a semipermeable barrier, the lymphatic endothelial cells regulate the sorting of lymph-borne antigens to the lymph node parenchyma and can themselves serve as antigen-presenting cells. The leukocytes entering the lymph node via the sinus system and the lymphocytes egressing from the parenchyma migrate through the lymphatic endothelial cell layer. The sinus lymphatic endothelial cells also orchestrate the organogenesis of lymph nodes, and they undergo bidirectional signalling with other sinus-resident cells, such as subcapsular sinus macrophages, to generate a unique lymphatic niche. In this Review, we consider the structural and functional basis of how the lymph node sinus system coordinates immune responses under physiological conditions, and in inflammation and cancer. Recent single-cell studies have revealed a previously unappreciated heterogeneity among endothelial cells that line the lymphatic sinuses of the lymph nodes. In this Review, the authors describe these various lymphatic endothelial cell types and how they support the trafficking of cells and antigens through lymph nodes.
Germinal center (GC) B cells are essential to generating protective antibody responses and are selected through a process of affinity maturation. Kwak et al . now define intrinsic properties of human GC B cells that are critical to antigen affinity discrimination. They identified BCR-containing actin-rich pod-like structures that facilitated formation of highly stable synapses and antigen internalization but only when GC B cells engaged high-affinity antigens. These findings reveal the importance of these structures in setting thresholds for affinity selection and driving GC B cell responses.
Protective antibody responses to vaccination or infection depend on affinity maturation, a process by which high-affinity germinal center (GC) B cells are selected on the basis of their ability to bind, gather, and present antigen to T follicular helper (Tfh) cells. Here, we show that human GC B cells have intrinsically higher-affinity thresholds for both B cell antigen receptor (BCR) signaling and antigen gathering as compared with naïve B cells and that these functions are mediated by distinct cellular structures and pathways that ultimately lead to antigen affinity– and Tfh cell–dependent differentiation to plasma cells. GC B cells bound antigen through highly dynamic, actin- and ezrin-rich pod-like structures that concentrated BCRs. The behavior of these structures was dictated by the intrinsic antigen affinity thresholds of GC B cells. Low-affinity antigens triggered continuous engagement and disengagement of membrane-associated antigens, whereas high-affinity antigens induced stable synapse formation. The pod-like structures also mediated affinity-dependent antigen internalization by unconventional pathways distinct from those of naïve B cells. Thus, intrinsic properties of human GC B cells set thresholds for affinity selection.
Lymph nodes are meeting points for circulating immune cells. A network of reticular cells that ensheathe a mesh of collagen fibers crisscrosses the tissue in each lymph node.
Composition of lymphocyte subpopulations in normal canine #lymph_nodes by cytology, multi-color flow cytometry, PARR http://t.co/jdP76fpWmj
|
 Your new post is loading...
Your new post is loading...
 Your new post is loading...
Your new post is loading...


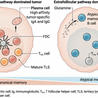












T helper 2 (Th2) responses protect against pathogens while also driving allergic inflammation, yet how large-scale Th2 responses are generated in tissue context remains unclear. Here, we used quantitative imaging to investigate early Th2 differentiation within lymph nodes (LNs) following cutaneous allergen administration. Contrary to current models, we observed extensive activation and “macro-clustering” of early Th2 cells with migratory type-2 dendritic cells (cDC2s), generating specialized Th2-promoting microenvironments. Macro-clustering was integrin-mediated and promoted localized cytokine exchange among T cells to reinforce differentiation, which contrasted the behavior during Th1 responses. Unexpectedly, formation of Th2 macro-clusters was dependent on the site of skin sensitization. Differences between sites were driven by divergent activation states of migratory cDC2 from different dermal tissues, with enhanced costimulatory molecule expression by cDC2 in Th2-generating LNs promoting prolonged T cell activation, macro-clustering, and cytokine sensing. Thus, the generation of dedicated Th2 priming microenvironments through enhanced costimulatory molecule signaling initiates Th2 responses in vivo and occurs in a skin site-specific manner.