Genome-wide association study of survival from sepsis due to pneumonia: #COPD The Lancet http://t.co/x7kQfa5YnG
Research and publish the best content.
Get Started for FREE
Sign up with Facebook Sign up with X
I don't have a Facebook or a X account
Already have an account: Login
Teaching and Learning Immunology. Information you never would have searched for!
Curated by
Gilbert C FAURE
 Your new post is loading... Your new post is loading...
 Your new post is loading... Your new post is loading...
|
|


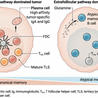





Interpretation
We have identified common variants in the FER gene that associate with a reduced risk of death from sepsis due to pneumonia. The FER gene and associated molecular pathways are potential novel targets for therapy or prevention and candidates for the development of biomarkers for risk stratification.
Entrez Gene summary for FER Gene:
Fer protein is a member of the FPS/FES family of nontransmembrane receptor tyrosine kinases. It regulate cell-cell adhesion and mediates signaling from the cell surface to the cytoskeleton via growth factor receptors. (provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008)GeneCards Summary for FER Gene:
FER (fer (fps/fes related) tyrosine kinase) is a protein-coding gene. Diseases associated with FER include sarcoma, and encephalitis. GO annotations related to this gene include lipid binding and actin binding. An important paralog of this gene is TEC.
UniProtKB/Swiss-Prot: FER_HUMAN, P16591Function: Tyrosine-protein kinase that acts downstream of cell surface receptors for growth factors and plays a role in the regulation of the actin cytoskeleton, microtubule assembly, lamellipodia formation, cell adhesion, cell migration and chemotaxis. Acts downstream of EGFR, KIT, PDGFRA and PDGFRB. Acts downstream of EGFR to promote activation of NF-kappa-B and cell proliferation. May play a role in the regulation of the mitotic cell cycle. Plays a role in the insulin receptor signaling pathway and in activation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase.
Acts downstream of the activated FCER1 receptor and plays a role in FCER1 (high affinity immunoglobulin epsilon receptor)-mediated signaling in mast cells. Plays a role in the regulation of mast cell degranulation. Plays arole in leukocyte recruitment and diapedesis in response to bacterial lipopolysaccharide (LPS). Plays a role in synapse organization, trafficking of synaptic vesicles, the generation of excitatory postsynaptic currents and neuron-neuron synaptic transmission. Plays a role in neuronal cell death after brain damage. Phosphorylates CTTN,
CTNND1, PTK2/FAK1, GAB1, PECAM1 and PTPN11. May phosphorylate JUP and PTPN1. Can phosphorylate STAT3, but the biological relevance of this depends on cell type and stimulus